CLOUD
10-Feb-202512-Feb-2025
VPS Images for Creating or Archiving Servers
1.What are VPS Images?
VPS Images are complete copies of your virtual servers that remain available even after the original server is deleted. Unlike snapshots that are tied to an active server, VPS Images serve as templates you can use to provision new servers or apply to existing ones.They are particularly valuable when you need to replicate servers with their operating system, applications and databases for multiple customers or projects. They reduce costs in cases when server needs to be archived for future use without keeping it active.For companies that develop or integrate business applications, VPS Images make it faster to provision new customers. Set up your applications and systems once and maintain different versions for various product tiers or customer requirements. When you get a new customer, deploying their application environment takes minutes instead of hours, speeding up delivery and ensuring consistency in project implementations.For those that manage multiple similar servers, VPS Images cut down setup time significantly. Instead of starting from scratch each time, you can roll out identical setups from your saved configurations.2.Managing VPS Images
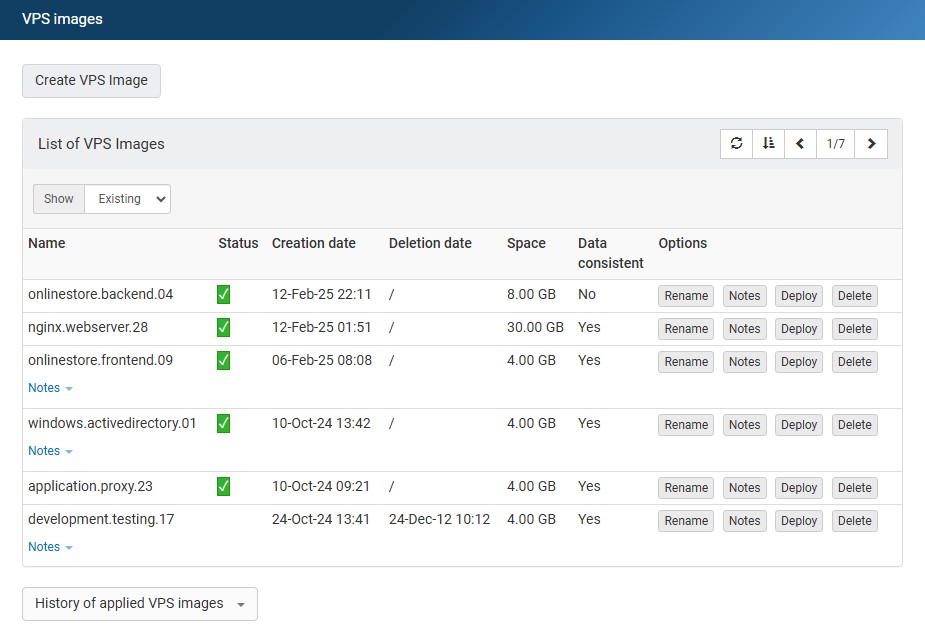
Within the My Interspace control panel, the VPS Images service includes tools for managing existing VPS Images. This user interface presents a detailed table listing each VPS Image, including creation and deletion dates, storage size, data consistency status and available actions such as Deploy, Delete, Rename, and Notes.- Deploy - Replace your server with the state captured in a selected VPS Image.
- Delete - Remove the VPS Image.
- Rename - Assign custom names to your VPS Images for easier identification, facilitating quicker access and organization.
- Notes - Add custom notes to each VPS Images, allowing you to record important details or reminders about the VPS Image's purpose or contents.
3.Creating VPS Images
Creating VPS Images is intuitive and straightforward. Simply, sign into the My Interspace control panel and open the VPS Images service. To create a VPS Image, click the Create VPS Image button.You will be prompted to select from what server to create the VPS Image, as well as to enter a custom name to your VPS Image for easier identification.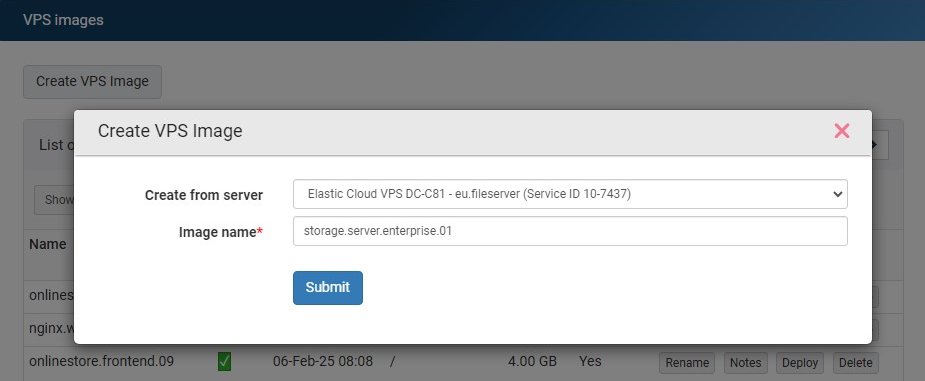
4.Installing VPS Images on Existing Servers
To install a VPS Image on an existing server, open the VPS Images service, locate the VPS Image, and click Deploy. You will be prompted to select the server where you want to install the VPS Image.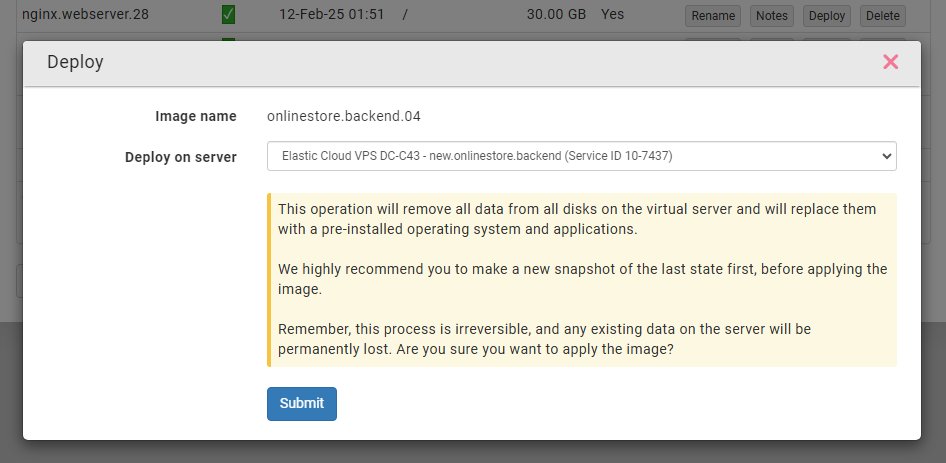
5.Installing VPS Images on New Servers
When ordering a new virtual server, you can use your VPS Image. In the Operating system section of the order form, select the Your VPS Images tab and choose your desired VPS Image. This will install the selected VPS Image on your new server when it is created.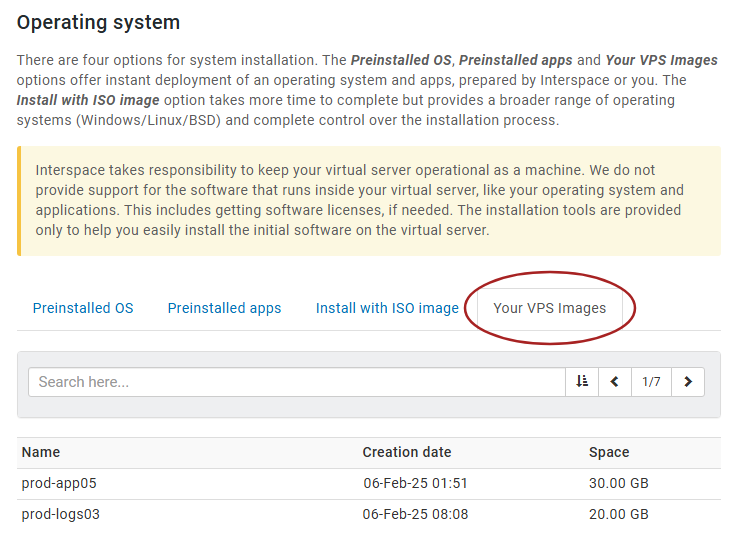
6.History of applied VPS images
Accessible via the History of applied VPS images button within the VPS Images service, this user interface provides a comprehensive overview of all past deployment processes. Upon accessing the history, users are presented with a detailed table that lists each deployed VPS Image by its name, alongside the date and time when the deployment was executed.7.Data Consistency
When Interspace Cloud creates VPS Images, it prioritizes creating a copy of the server with data consistency, aiming to capture the system's state at a moment when all data is synchronized and disk operations are completed. This approach ensures a seamless restoration to a specific point in time, without the need for additional data checks or adjustments.It's important to note that some older operating systems, like Linux and Windows versions produced before 2012, may not support the creation of a data-consistent copy. In such instances, Interspace Cloud will create a copy without data consistency. These copies can still be used to restore the server to a specific point in time. However, starting the server after restoration may be similar to booting a system after a forced restart while it was running. This occasionally requires performing data integrity checks, such as verifying disk consistency.Related content
Documentation

Cloud
Communications

Hosting

My Interspace
Tech Articles

Tutorials

Learn
News

Latest news

Latest events
Related products

Elastic Cloud VPS
Elastic Cloud VPS is a virtual machine running on advanced cloud and networking technologies, offering superior advantages over traditional VPS hosting at an exceptional price-to-performance ratio.
Deploy OS and apps in just 1 min. One-click geo-redundant backups, snapshots and disaster recovery. Next-generation AMD EPYC processors, ultra-fast NVMe storage, dedicated connections and free private networking.

[OLD] Cloud VPN PointConnect
Cloud VPN enables individual computers to securely connect to your cloud private network from anywhere in the world, by encrypting data as it travels over the Internet. Once connected, they can access any of your virtual or dedicated servers, as well as metro Ethernet endpoints using their private IPs.
It's perfect for providers of CRM, ERP and services alike, who want to provide secure access to their apps over the Internet.
Cloud NАТ Gateway
Inbound and outbound connections over the Internet, for your virtual servers that have only private IP addresses.
The servers access the Internet by routing the traffic through the NAT gateway. Optionally, they can receive inbound connections from the Internet using the port forwarding feature.
 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Македонски
Македонски Slovenščina
Slovenščina Srpski
Srpski Shqip
Shqip Български
Български